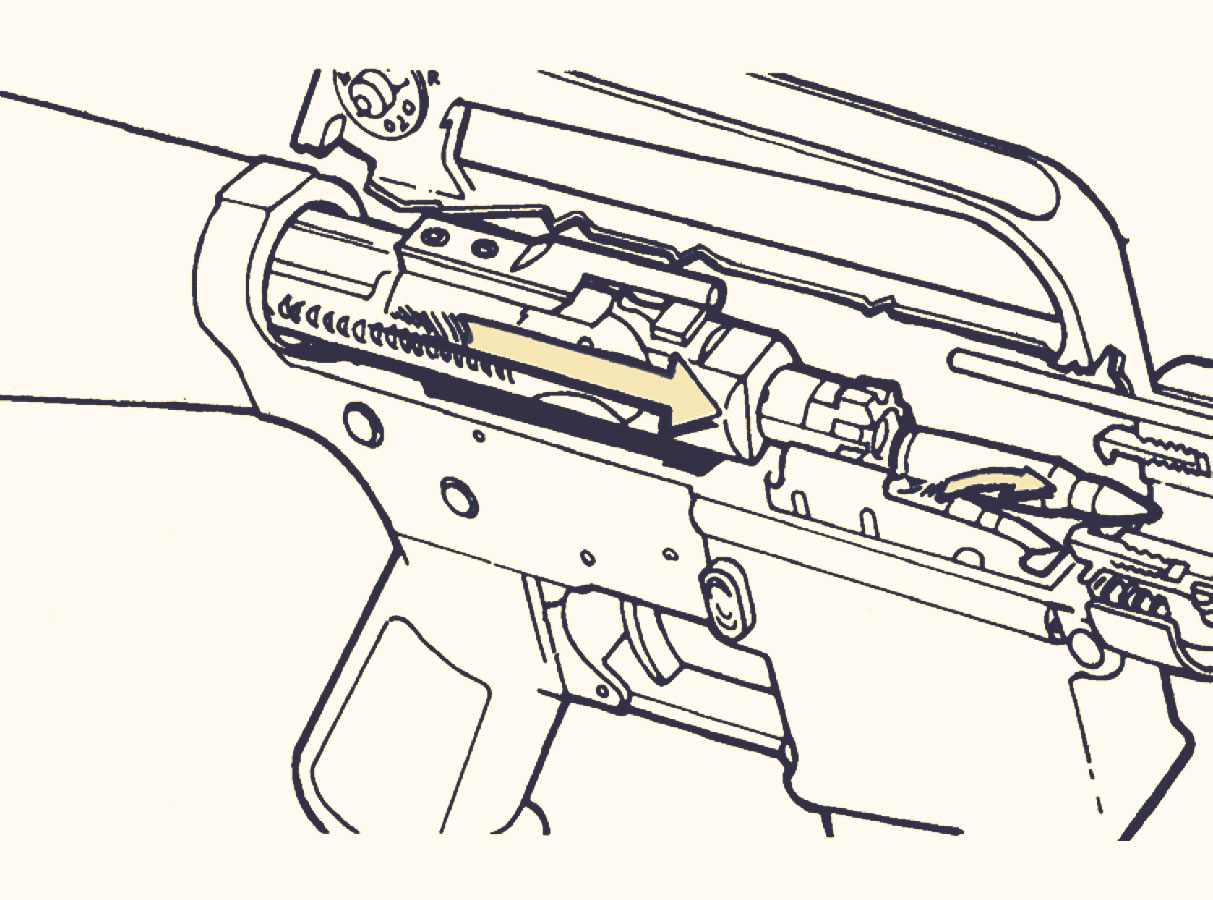
A bolt carrier group (BCG) is a critical component of an AR-15 rifle. Its main purpose is to ensure that the bolts and cartridges are properly locked in place and ready to fire. The BCG also cocks the hammer and returns the striker to its forward position after each shot has been fired.
To understand how a BCG works, it is first important to understand the basic components of an AR-15 rifle. The AR-15 rifle is a gas-operated firearm that uses hot gases from the burning propellant to cycle the action. This means that when a round is fired, hot gases from the burning powder propel the bullet down the barrel and into the chamber. At the same time, these hot gases push against the bolt carrier group, which is located behind the chamber.
The bolt carrier group consists of the bolt carrier, the bolt, and the gas key. The bolt carrier is a heavy piece of metal that houses the bolt. The bolt is what locks into place and engages with the chamber. The gas key is a small piece of metal that is attached to the bolt carrier and allows gas to enter the chamber and push against the bolt.
When a round is fired, hot gases from the burning powder travel down the barrel and into the chamber. These gases push against the back of the bolt, which causes the bolt carrier group to move rearward. As the bolt carrier group moves rearward, it extracts the spent cartridge from the chamber and ejects it out of the rifle. At the same time, the bolt carrier group cocks the hammer and returns the striker to its forward position.
The bolt carrier group is an important component of an AR-15 rifle because it ensures that the bolts and cartridges are properly locked in place and ready to fire. It also cocks the hammer and returns the striker to its forward position after each shot has been fired.