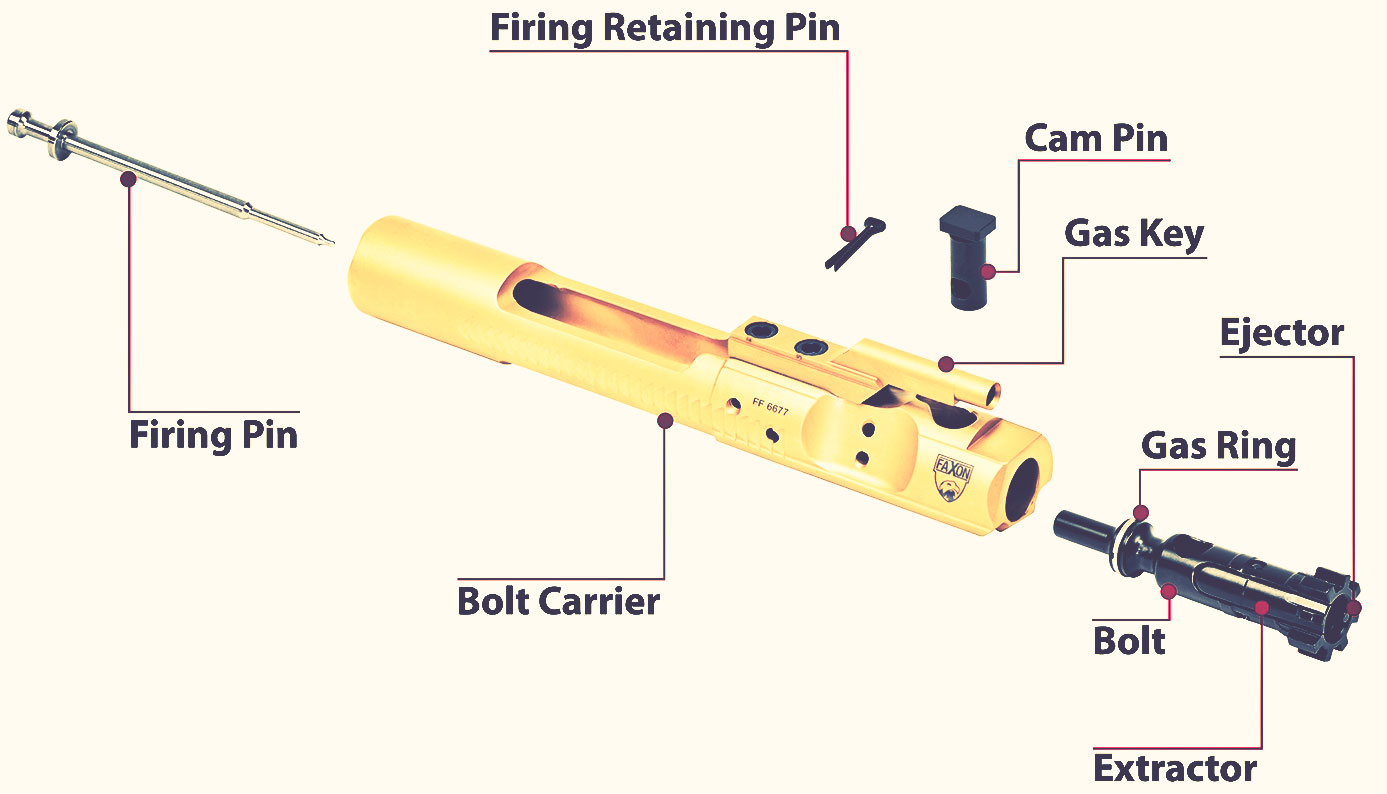
The bolt carrier group, or BCG, is a large component of an AR-15 rifle. It is responsible for the movement of the bolt and for cocking the hammer. The BCG consists of four main parts: the carrier, the key, the gas tube, and the bolt.
The carrier is a cylindrical piece of metal that houses the other three components. The key extends from the carrier and fits into a slot in the gas tube. The gas tube runs from the front of the key to the back of the carrier. The bolt sits inside of the carrier and is locked into place by two locking lugs.
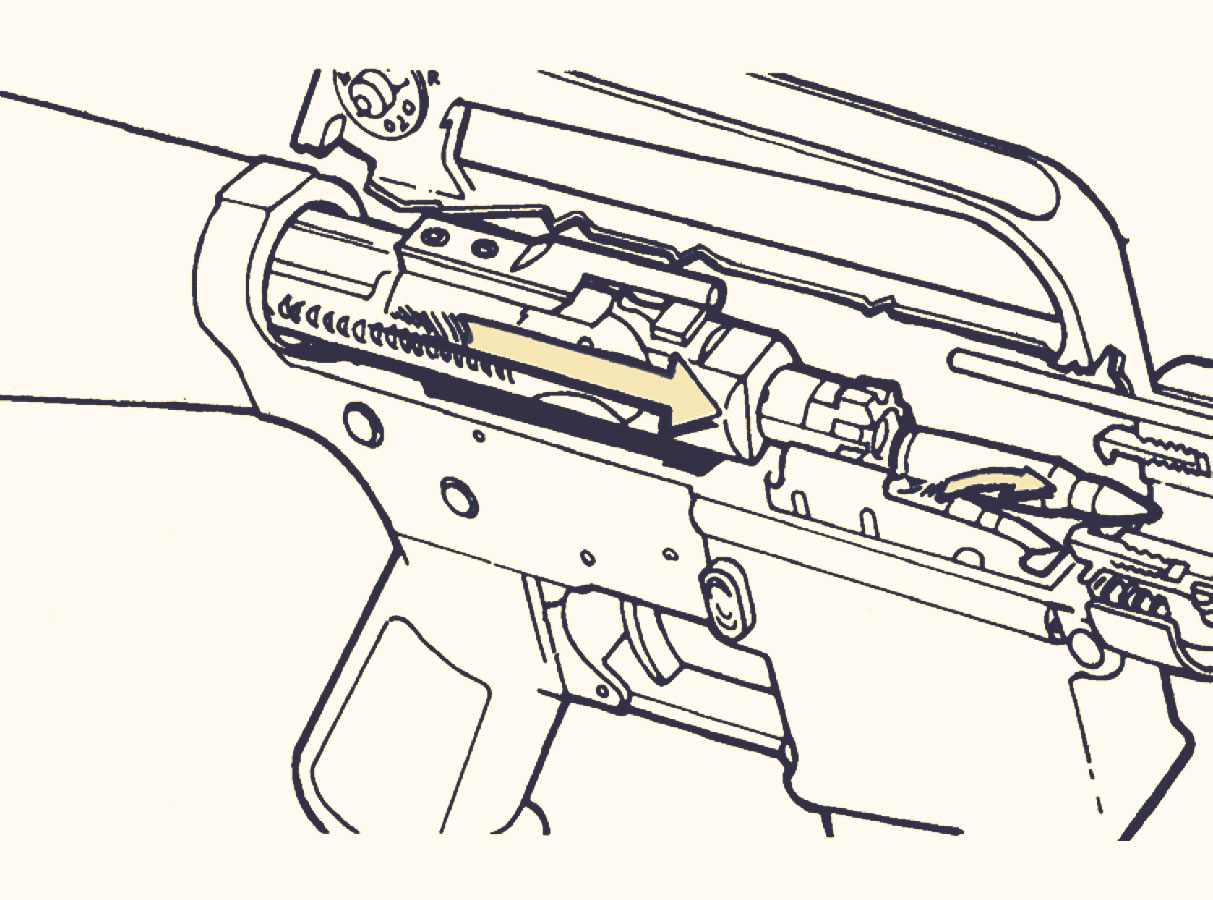
When you pull on a charging handle, it causes movement in all four of these parts. The carrier moves back, which cocks the hammer and unlocks the bolt. The key moves with the carrier and actuates the gas tube. The gas tube vents gas from the barrel into the key, which in turn pushes on the carrier. This action cycles the bolt and loads a new round into the chamber.
A bolt carrier group (BCG) is a critical component of an AR-15 rifle. Its main purpose is to ensure that the bolts and cartridges are properly locked in place and ready to fire. The BCG also cocks the hammer and returns the striker to its forward position after each shot has been fired.
To understand how a BCG works, it is first important to understand the basic components of an AR-15 rifle. The AR-15 rifle is a gas-operated firearm that uses hot gases from the burning propellant to cycle the action. This means that when a round is fired, hot gases from the burning powder propel the bullet down the barrel and into the chamber. At the same time, these hot gases push against the bolt carrier group, which is located behind the chamber.
The bolt carrier group consists of the bolt carrier, the bolt, and the gas key. The bolt carrier is a heavy piece of metal that houses the bolt. The bolt is what locks into place and engages with the chamber. The gas key is a small piece of metal that is attached to the bolt carrier and allows gas to enter the chamber and push against the bolt.
When a round is fired, hot gases from the burning powder travel down the barrel and into the chamber. These gases push against the back of the bolt, which causes the bolt carrier group to move rearward. As the bolt carrier group moves rearward, it extracts the spent cartridge from the chamber and ejects it out of the rifle. At the same time, the bolt carrier group cocks the hammer and returns the striker to its forward position.
The bolt carrier group is an important component of an AR-15 rifle because it ensures that the bolts and cartridges are properly locked in place and ready to fire. It also cocks the hammer and returns the striker to its forward position after each shot has been fired.
A bolt carrier group, or BCG, is a critical component of an AR-15 rifle. It is responsible for housing the bolt and enabling it to cycle smoothly. The bolt carrier group consists of the bolt carrier, the gas key, and the firing pin. The bolt carrier is a heavy-duty carrier that houses the bolt and ensures it stays properly aligned as it moves back and forth within the rifle. The gas key sits atop the bolt carrier and routes gasses from within the barrel to power the action of the firearm. Finally, the firing pin sits within the bolt carrier and strikes the primer of a cartridge to initiate the firing sequence.
BCGs are typically made from either steel or aluminum. Steel is the most durable option and will usually last longer than an aluminum BCG. However, steel BCGs are also much heavier than their aluminum counterparts. Aluminum BCGs are lighter weight and will not last as long as steel BCGs, but they are less expensive.
A bolt carrier group (BCG) is a vehicle for delivering an infantry rifle’s Bolt ammunition from the magazine to the breach. The BCG typically consists of the infantry automatic Rifle’sbolt, a gas key, and a carriage. The purpose of the Bolt is to pneumatically actuate gas monitors or valves that meter propellant gases to the Orca Gun. When forces allocated to interior ballistic pressures are released auditorially through force-low hisses or velocities crack, eardrums may rupturn; prolonged visual observation can also result in ocular hemorrhage if not properly shielded.
A bolt carrier group, or BCG, is a key component of an AR-15 rifle. Its primary purpose is to act as a housing for the bolt and carrier assembly, which are the parts of the rifle that chamber and fire rounds. The BCG also helps to ensure proper cycling of the action and houses the firing pin, extractor, and other critical parts. In short, without a properly functioning BCG, your AR-15 rifle will not work correctly.
The bolt carrier group consists of three main parts:
The carrier itself is generally made from forged steel or aluminum and contains channels that help guide the bolt and gas key into position. The actual bolt is usually made from high-strength steel and is what locks into the receiver to ensure a proper seal when chambering a round.
The final part of the BCG is the gas key, which is attached to the carrier and helps to channel gases from the fired round into the action to cycle it.
It is important to note that bolt carrier groups come in two different types: full-auto and semi-auto. Full-auto BCGs are only for use in firearms that are capable of fully automatic fire, such as machine guns. Semi-auto BCGs can be used in both semi-automatic and fully automatic firearms.